In India, the public authority fund-raises to support its exercises by giving different kinds of protections to general society. One such security is known as a “G-Sec” or government security, which is basically a bond given by the government.
Treasury bills, or “T-bills” for short, are a kind of G-Sec that have a development of short of what one year (normally 91 days, 182 days or 364 days). They are given at a rebate to their presumptive worth and mature at face esteem, implying that the financial backer procures the distinction between the price tag and the assumed worth as interest.
T-bills are viewed as one of the most secure investment choices in India, as they are upheld by the public authority and convey no credit risk. They are additionally profoundly liquid, implying that they can be handily traded on the lookout.
People, organizations, banks, and other monetary establishments can all put invest into T-bills, making them a famous investment choice in India.
For latest Calendar for Auction of Government of India Treasury Bills as of March 29, 2023
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/PressRelease/PDFs/PR19379F7979822B304EB29BB00FD3C9D13585.PDF
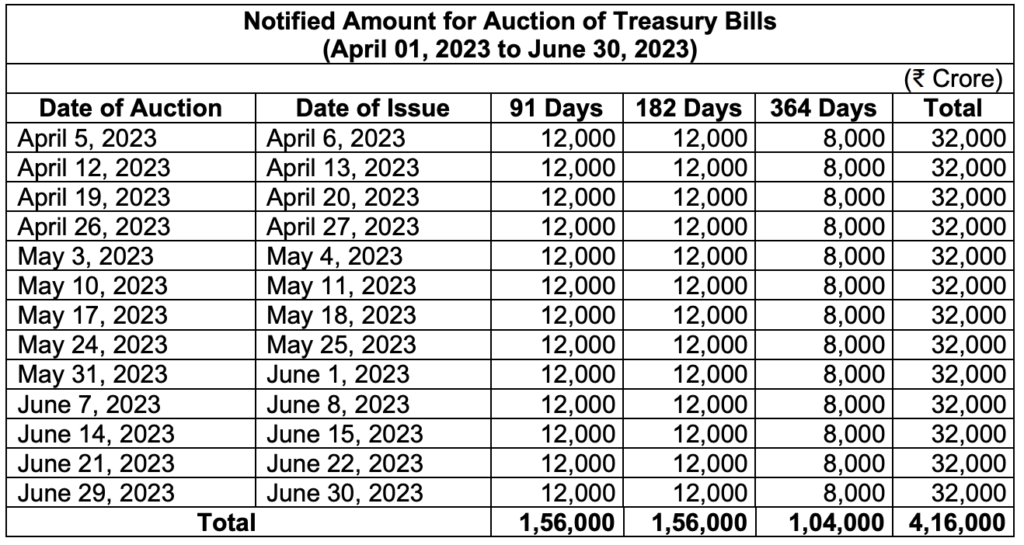
Source : RBI
Advantages of T-Bills:
- Safety: T-bills are considered to be one of the safest investments as they are backed by the government, which makes them free from credit risk.
- Liquidity: T-bills are highly liquid, which means that they can be easily bought and sold in the market, providing investors with flexibility and the ability to access cash when needed.
- Short-term investment: T-bills are short-term investments that mature within a year, which makes them an ideal option for investors who prefer short-term investments or who need to access cash quickly.
- Low-risk investment: Since T-bills are backed by the government, they are considered to be low-risk investments, which makes them a popular investment option for conservative investors.
Disadvantages of T-Bills:
- Low return on investment: The return on investment for T-bills is relatively low compared to other investment options, which makes them less attractive to investors who are looking for higher returns.
- Interest rate risk: The value of T-bills can be affected by changes in interest rates, which means that investors may face interest rate risk.
- Inflation risk: T-bills returns may not keep pace with inflation, which means that investors may end up losing purchasing power over time.
- Limited investment period: T-bills have a fixed maturity period, which means that investors who want to hold investments for a longer period may need to consider other investment options.
How to invest in T-Bills:
- Open a Demat Account: To invest in T-bills, you need to open a Demat account with a registered depository participant (DP) like a bank, broker or financial institution. This account will hold your T-bills in electronic form.
- Check the Auction Calendar: T-bills are issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) through auctions held on a regular basis. You need to check the auction calendar on the RBI’s website or in the financial newspapers to know when the auctions are taking place.
- Place Bids: On the day of the auction, you need to place a bid through your DP. You can place the bid either through your DP’s online platform or by submitting a physical application form.
- Bid Price: You need to specify the bid price, which is the amount you are willing to pay for the T-bill. The bid price is quoted as a percentage of the face value of the T-bill.
- Allocation of T-Bills: The RBI will allocate the T-bills to the successful bidders based on the bid price. If your bid is successful, you will receive a confirmation of the allotment.
- Payment: You need to make payment for the T-bills on the date of allotment. The payment can be made either through your DP’s online platform or by submitting a physical payment instruction.
- Holding Period: T-bills have a holding period, after which they mature and the face value is paid to the investor. You can hold T-bills until maturity or sell them in the secondary market.
Where to buy T-Bills
You can buy T-bills from Many platforms, I personally use COIN by Zerodha
Download Coin from here and start investing
How T-bills are taxed in India
As far as I know:
- Interest Income Tax: The interest earned on T-bills is taxable as per the Income Tax Act, 1961. The tax is deducted at source (TDS) by the government, and the rate of TDS is currently 7.5% for individuals and 20% for companies. However, if your total income is below the taxable limit, you can submit Form 15G/15H to your DP to avoid TDS.
- Capital Gains Tax: If you sell your T-bills in the secondary market before maturity, any capital gains you make will be subject to capital gains tax. The tax rate depends on the holding period of the T-bills. If you sell the T-bills within one year of purchase, the gains will be treated as short-term capital gains and taxed at your income tax slab rate. If you sell the T-bills after one year, the gains will be treated as long-term capital gains and taxed at a flat rate of 10%.
Please refer to RBI site for more information : https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/BS_PressReleaseDisplay.aspx?prid=55434


